OpenROAD#
About OpenROAD#
OpenROAD is the leading open-source, foundational application for semiconductor digital design. The OpenROAD flow delivers an Autonomous, No-Human-In-Loop (NHIL) flow, 24 hour turnaround from RTL-GDSII for rapid design exploration and physical design implementation.
OpenROAD Mission#
OpenROAD eliminates the barriers of cost, schedule risk and uncertainty in hardware design to promote open access to rapid, low-cost IC design software and expertise and system innovation. The OpenROAD application enables flexible flow control through an API with bindings in Tcl and Python.
OpenROAD is used in research and commercial applications such as,
Hammer from UC Berkeley
OpenFASoC from IDEA-FASoC for mixed-signal design flows
OpenROAD fosters a vibrant ecosystem of users through active collaboration and partnership through software development and key alliances. Our growing user community includes hardware designers, software engineers, industry collaborators, VLSI enthusiasts, students and researchers.
OpenROAD strongly advocates and enables IC design-based education and workforce development initiatives through training content and courses across several global universities, the Google-SkyWater shuttles also includes GlobalFoundries shuttles, design contests and IC design workshops. The OpenROAD flow has been successfully used to date in over 600 silicon-ready tapeouts for technologies up to 12nm.
Getting Started with OpenROAD-flow-scripts#
OpenROAD provides OpenROAD-flow-scripts as a native, ready-to-use prototyping and tapeout flow. However, it also enables the creation of any custom flow controllers based on the underlying tools, database and analysis engines. Please refer to the flow documentation here.
OpenROAD-flow-scripts (ORFS) is a fully autonomous, RTL-GDSII flow for rapid architecture and design space exploration, early prediction of QoR and detailed physical design implementation. However, ORFS also enables manual intervention for finer user control of individual flow stages through Tcl commands and Python APIs.
Figure below shows the main stages of the OpenROAD-flow-scripts:
Here are the main steps for a physical design implementation using OpenROAD;
FloorplanningFloorplan initialization - define the chip area, utilization
IO pin placement (for designs without pads)
Tap cell and well tie insertion
PDN- power distribution network creation
Global PlacementMacro placement (RAMs, embedded macros)
Standard cell placement
Automatic placement optimization and repair for max slew, max capacitance, and max fanout violations and long wires
Detailed PlacementLegalize placement - align to grid, adhere to design rules
Incremental timing analysis for early estimates
Clock Tree SynthesisInsert buffers and resize for high fanout nets
Optimize setup/hold timingGlobal RoutingAntenna repair
Create routing guides
Detailed RoutingLegalize routes, DRC-correct routing to meet timing, power constraints
Chip FinishingParasitic extraction using OpenRCX
Final timing verification
Final physical verification
Dummy metal fill for manufacturability
Use KLayout or Magic using generated GDS for DRC signoff
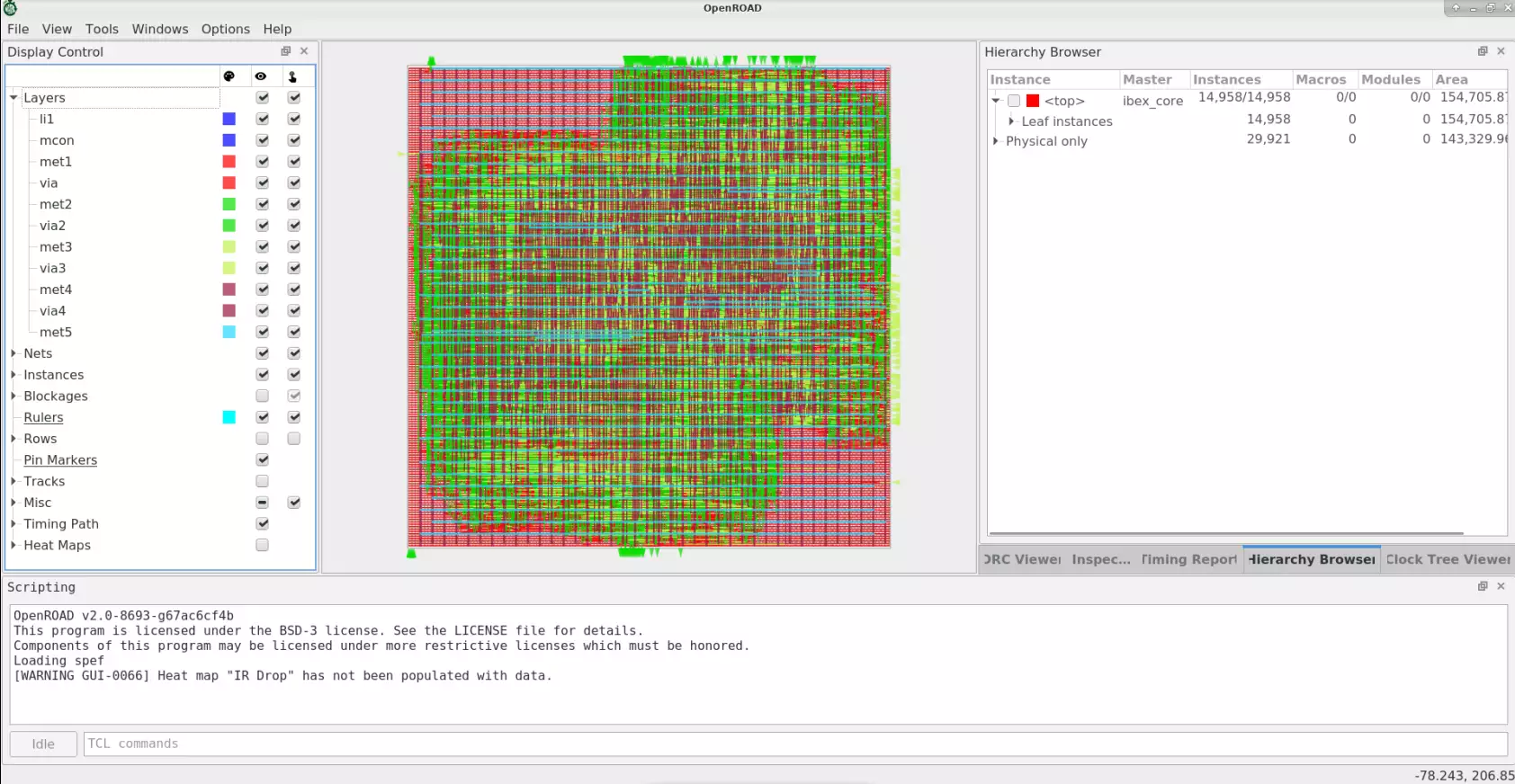
GUI#
The OpenROAD GUI is a powerful visualization, analysis, and debugging tool with a customizable Tcl interface. The below figures show GUI views for various flow stages including floorplanning, placement congestion, CTS and post-routed design.
Floorplan#
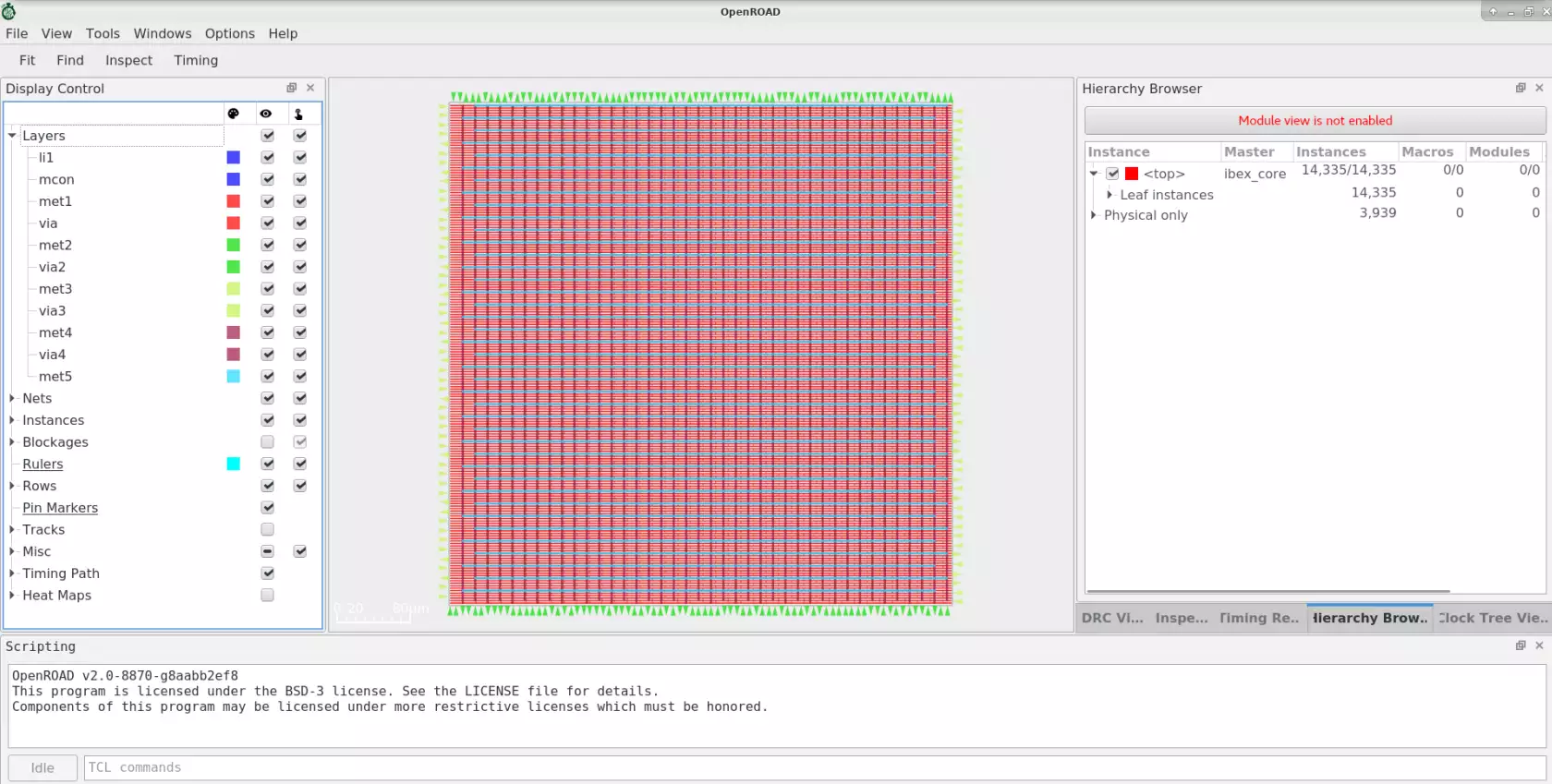
Automatic Hierarchical Macro Placement#
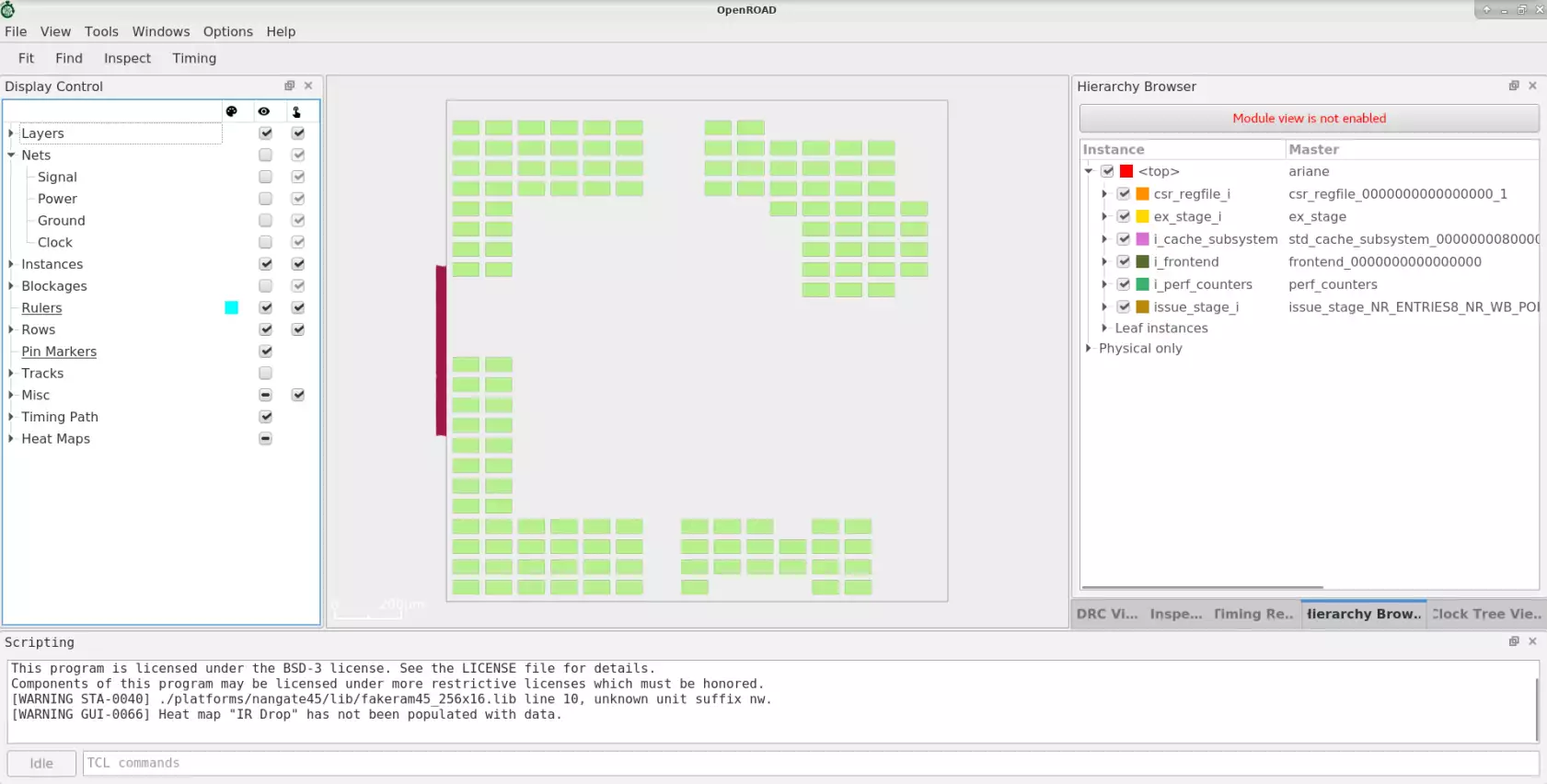
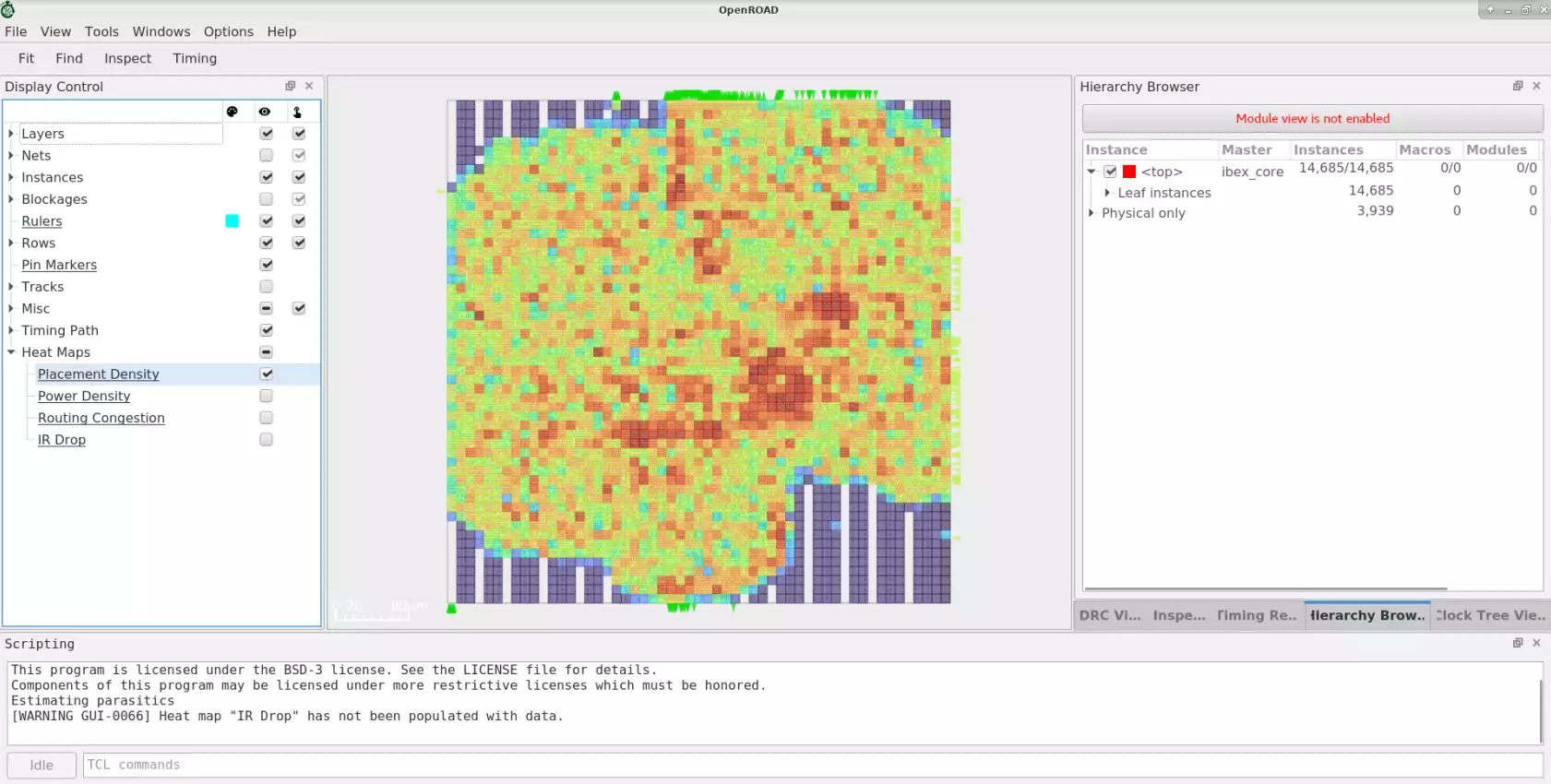
Placement Congestion Visualization#
CTS#
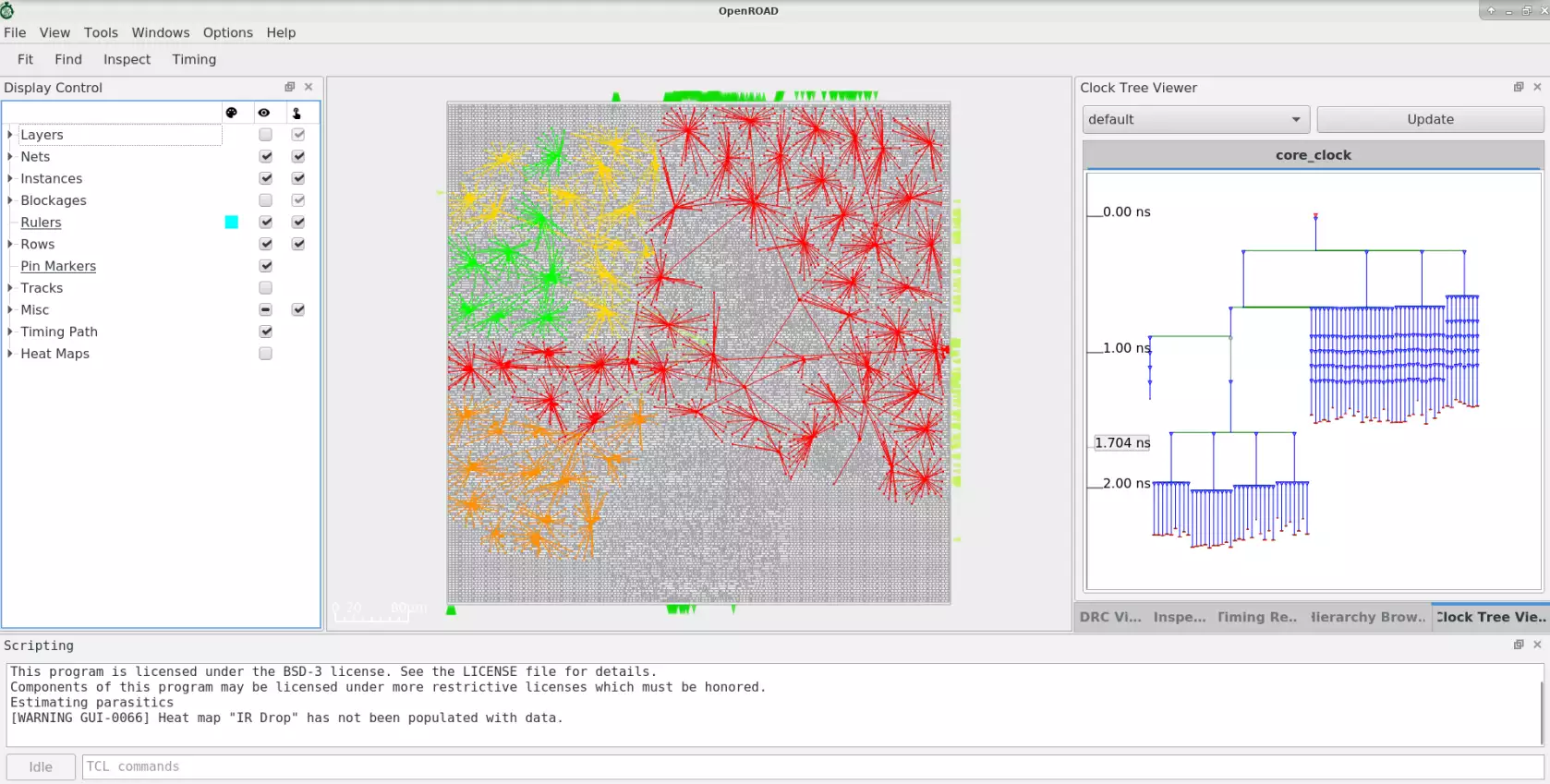
Routing#
PDK Support#
The OpenROAD application is PDK independent. However, it has been tested and validated with specific PDKs in the context of various flow controllers.
OpenLane supports SkyWater 130nm and GlobalFoundries 180nm.
OpenROAD-flow-scripts supports several public and private PDKs including:
Open-Source PDKs#
GF180- 180nmSKY130- 130nmNangate45- 45nmASAP7- Predictive FinFET 7nm
Proprietary PDKs#
These PDKS are supported in OpenROAD-flow-scripts only. They are used to test and calibrate OpenROAD against commercial platforms and ensure good QoR. The PDKs and platform-specific files for these kits cannot be provided due to NDA restrictions. However, if you are able to access these platforms independently, you can create the necessary platform-specific files yourself.
GF55- 55nmGF12- 12nmIntel22- 22nmIntel16- 16nmTSMC65- 65nm
Tapeouts#
OpenROAD has been used for full physical implementation in over 600 tapeouts in SKY130 and GF180 through the Google-sponsored, Efabless MPW shuttle and ChipIgnite programs.
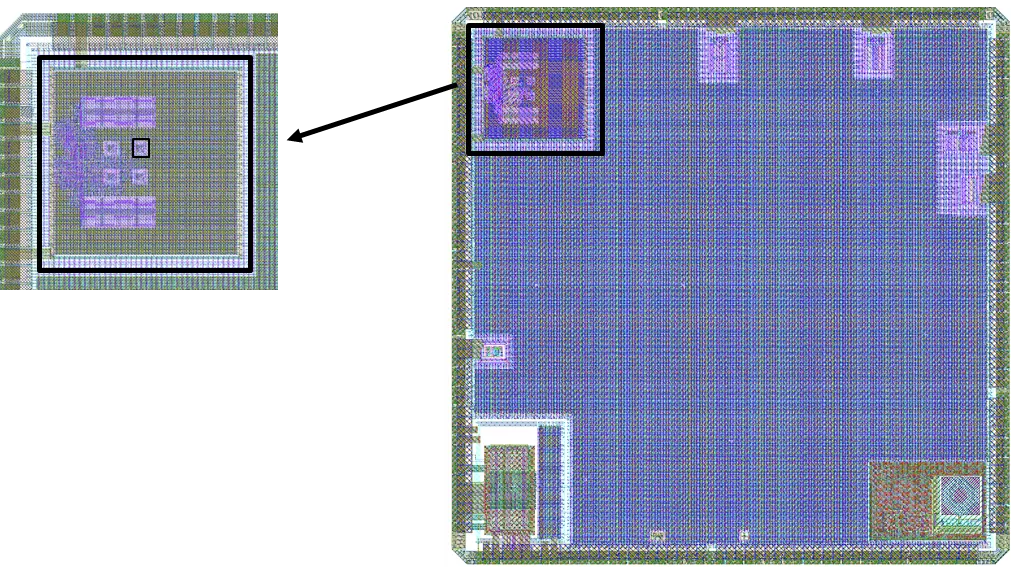
OpenTitan SoC on GF12LP - Physical design and optimization using OpenROAD#
Continuous Tapeout Integration into CI#
The OpenROAD project actively adds successfully taped out MPW shuttle designs to the CI regression testing. Examples of designs include Open processor cores, RISC-V based SoCs, cryptocurrency miners, robotic app processors, amateur satellite radio transceivers, OpenPower-based Microwatt etc.
Build OpenROAD#
To build OpenROAD tools locally in your machine, follow steps from here.
Regression Tests#
There are a set of executable regression test scripts in ./test/.
# run tests for all tools
./test/regression
# run all flow tests
./test/regression flow
# run <tool> tests
./test/regression <tool>
# run all <tool>-specific unit tests
cd src/<tool>
./test/regression
# run only <TEST_NAME> for <tool>
cd src/<tool>
./test/regression <TEST_NAME>
The flow tests check results such as worst slack against reference values.
Use report_flow_metrics [test]... to see all of the metrics.
% report_flow_metrics gcd_nangate45
insts area util slack_min slack_max tns_max clk_skew max_slew max_cap max_fanout DPL ANT drv
gcd_nangate45 368 564 8.8 0.112 -0.015 -0.1 0.004 0 0 0 0 0 0
To update a failing regression, follow the instructions below:
# update log files (i.e. *ok)
save_ok <TEST_NAME>
# update "*.metrics" for tests that use flow test
save_flow_metrics <TEST_NAME>
# update "*.metrics_limits" files
save_flow_metrics_limits <TEST_NAME>
Run#
openroad [-help] [-version] [-no_init] [-exit] [-gui]
[-threads count|max] [-log file_name] cmd_file
-help show help and exit
-version show version and exit
-no_init do not read .openroad init file
-threads count|max use count threads
-no_splash do not show the license splash at startup
-exit exit after reading cmd_file
-gui start in gui mode
-python start with python interpreter [limited to db operations]
-log <file_name> write a log in <file_name>
cmd_file source cmd_file
OpenROAD sources the Tcl command file ~/.openroad unless the command
line option -no_init is specified.
OpenROAD then sources the command file cmd_file if it is specified on
the command line. Unless the -exit command line flag is specified, it
enters an interactive Tcl command interpreter.
A list of the available tools/modules included in the OpenROAD app and their descriptions are available here.
Git Quickstart#
OpenROAD uses Git for version control and contributions. Get familiarised with a quickstart tutorial to contribution here.
Understanding Warning and Error Messages#
Seeing OpenROAD warnings or errors you do not understand? We have compiled a table of all messages and you may potentially find your answer here.
License#
BSD 3-Clause License. See LICENSE file.